Can hereditary hair loss be treated?
Can genetic hair loss be cured? This is one of the most frequently asked questions we receive. Hereditary hair loss, scientifically known as androgenetic alopecia or commonly known as male pattern baldness. This is a genetic predisposition that has a profound effect on the complicated process of hair growth. This hereditary predisposition disrupts the normal hair growth cycle, which leads to a significant shortening of the growth phase. In those affected, the hair spends less time actively growing and more time in the resting phase before it finally falls out.
The reason for genetic hair loss
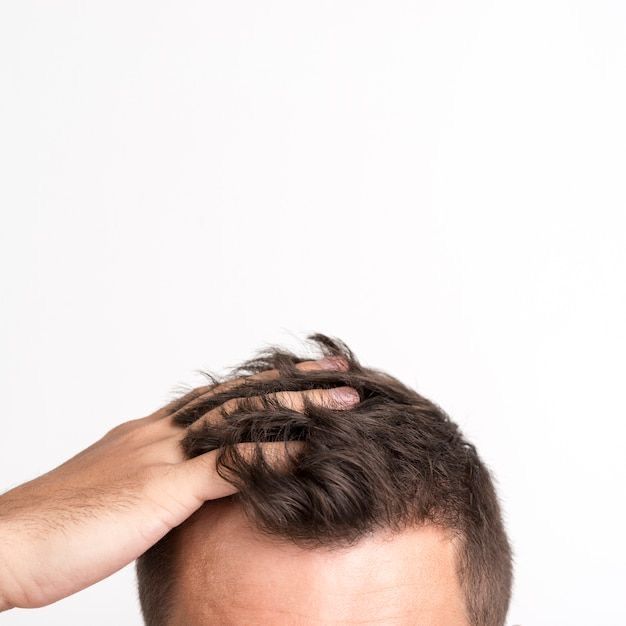
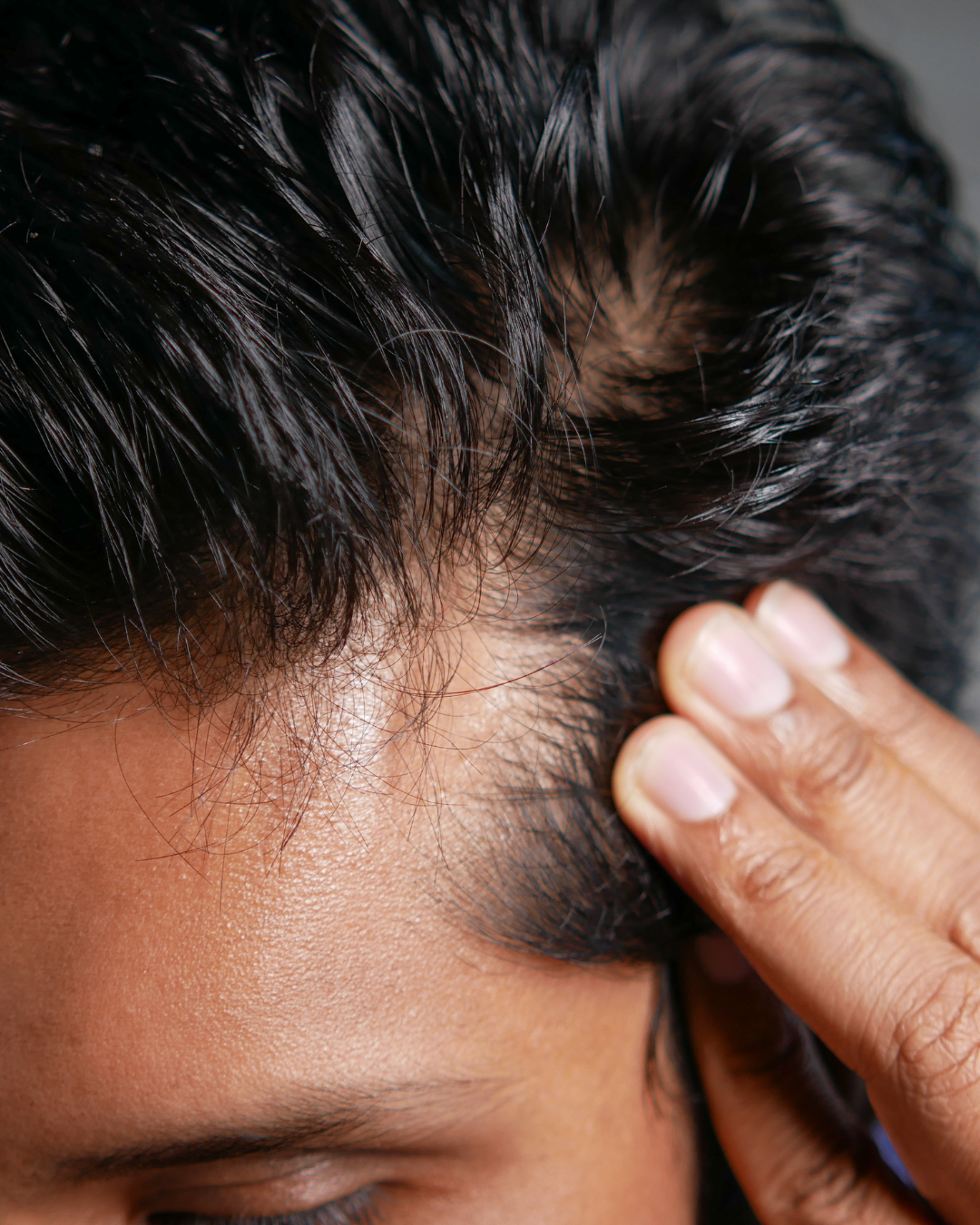
This characteristic pattern of hair loss usually begins with the temples and hairline receding over time. The receding hairline is often accompanied by a thinning of the crown, creating the characteristic horseshoe-shaped pattern associated with male pattern baldness. The cause of this condition lies in the interaction of genetic factors and hormonal activity, in particular the influence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) on the susceptible hair follicles.
The most common causes of hair loss
The reasons for hair loss are varied and can differ from person to person. In this article, we will focus on the topic of genetic hair loss, but here are some main reasons for hair loss:
- Genetics: family history can play a crucial role, especially in conditions such as male pattern baldness and female pattern baldness.
- Hormones: Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a major contributor to hair loss in people who are genetically predisposed to it.
- Environmental factors: stress, health problems, certain medications and even poor diet can lead to temporary hair loss.
- Medical conditions: Autoimmune conditions such as alopecia areata cause sudden, patchy hair loss.
- Medical treatments: Treatments such as chemotherapy can cause more shedding.
The reason for your hair loss may be one of these, or perhaps it's not on the books - in which case you may need specialist advice, which is free.
Why do I lose hair?
Do you really know why your hair is falling out? It is important to distinguish between hereditary hair loss and temporary hair loss caused by factors such as stress or certain medical treatments. In contrast to stress-related or temporary hair loss, hereditary hair loss follows a steady and predictable course. The genetic aspect of hereditary hair loss makes this type of hair loss more likely to occur in people with a family history of the condition. It can be inherited on both the maternal and paternal side, contributing to the complex genetic inheritance patterns associated with male pattern baldness.
Understanding this genetic basis is crucial for distinguishing between different forms of hair loss and for understanding the intricate ways in which genetics contribute to our physical characteristics.
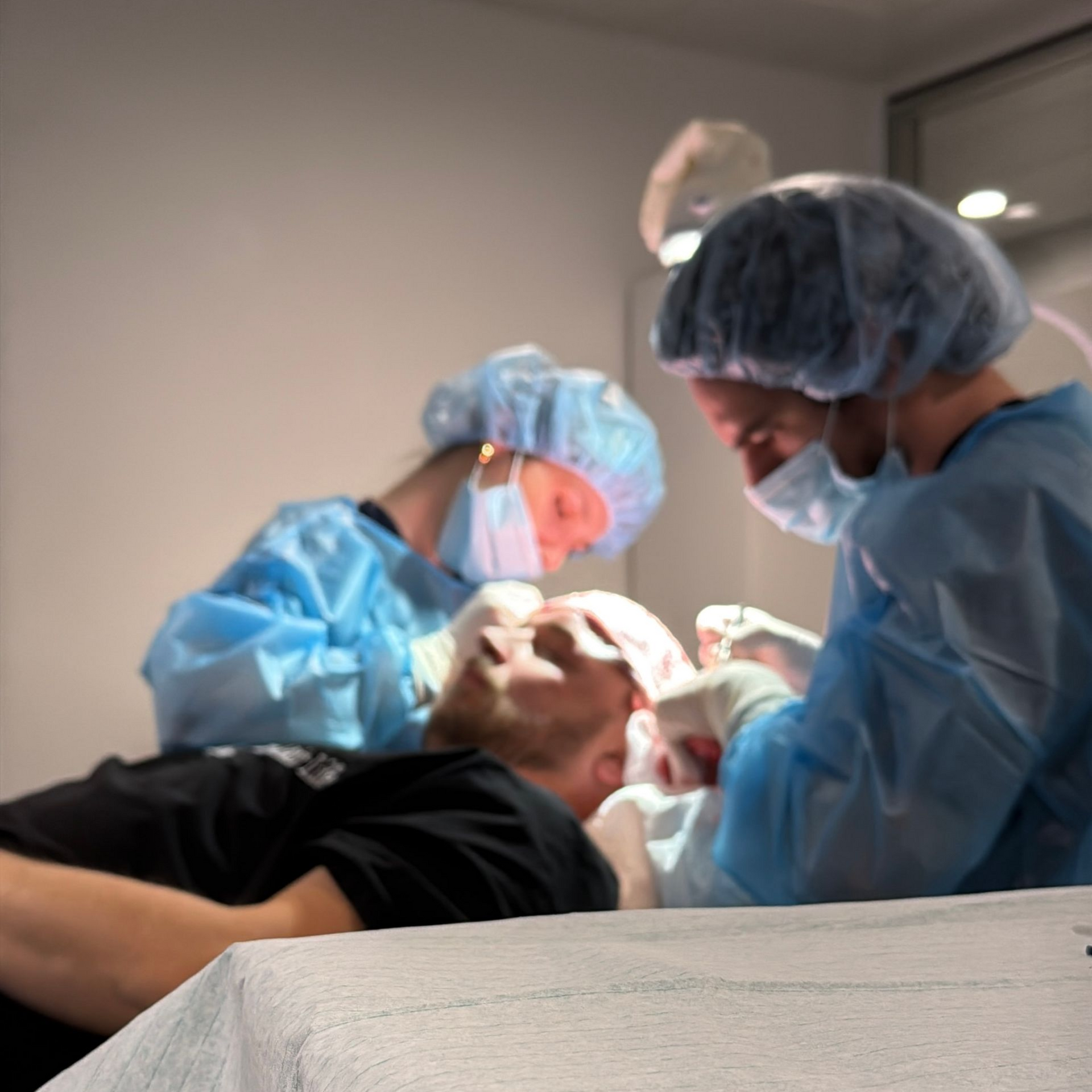
What can I try before a hair transplant?
Before considering a hair transplant, there are several methods that people often try to combat hair loss. These methods can vary in effectiveness and are often considered less invasive alternatives. Some of the common methods that should be tried before a hair transplant are:
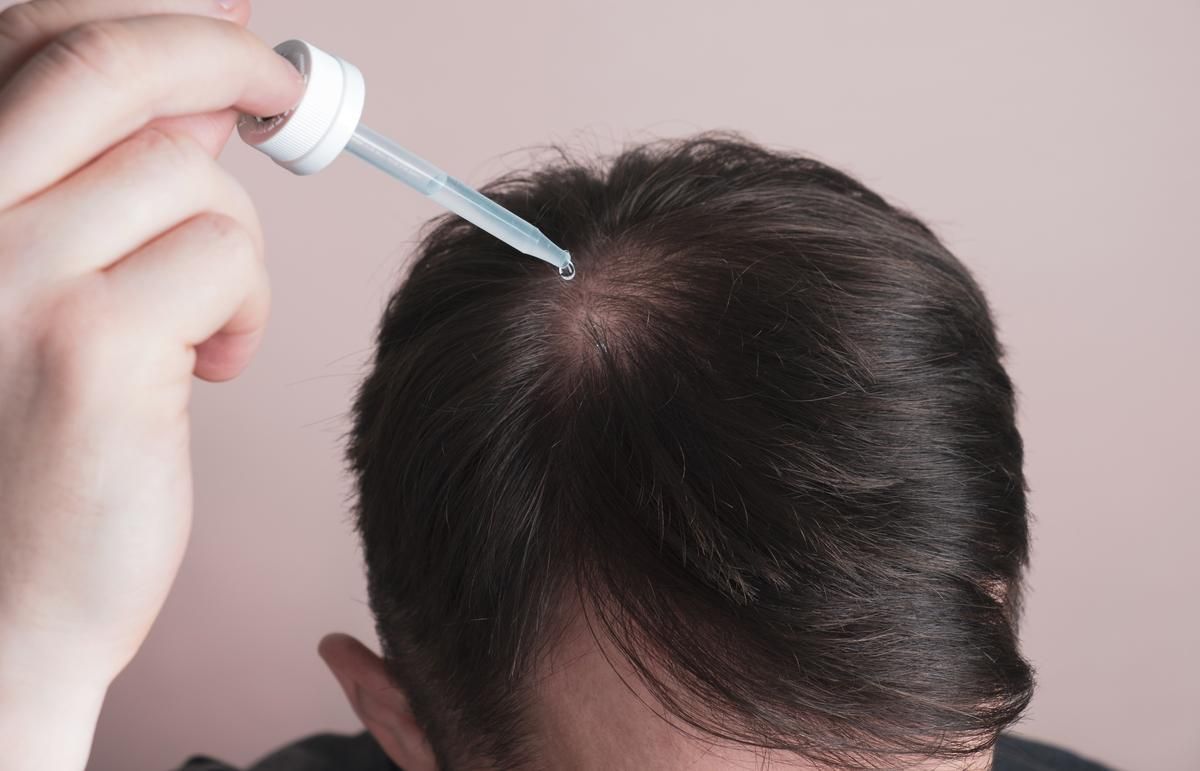
- Medication: there are medications such as minoxidil and finasteride that are designed to slow down hair loss and promote hair regrowth. Minoxidil is a topical solution that is applied directly to the scalp, while finasteride is an oral medication that inhibits the hormone responsible for hair loss.
- Low-level laser therapy (LLLT): Low-level lasers or light-emitting diodes are used to stimulate the hair follicles and promote hair growth.
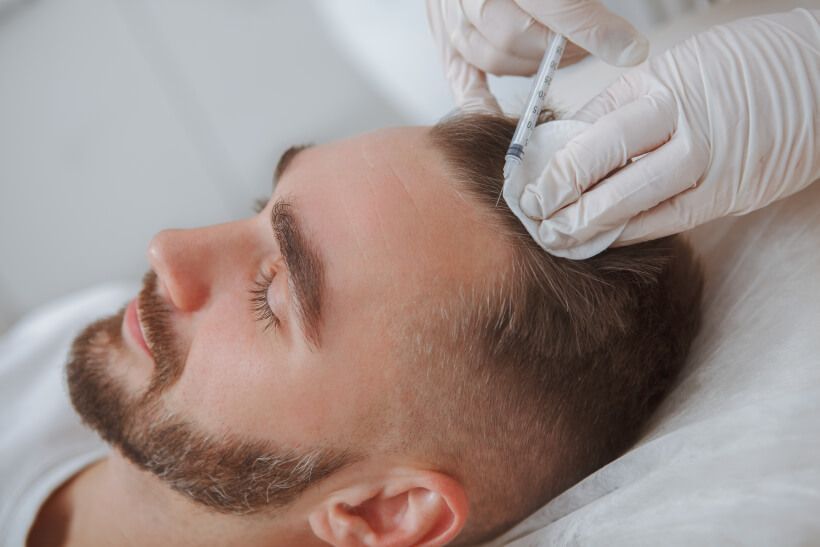
- Autologous blood treatment: In this therapy, a small amount of blood is taken from the patient, processed to concentrate the platelets and the platelet-rich blood component is then injected into the scalp. It is believed that this stimulates the hair follicles and promotes hair growth.
- Topical treatments: Various shampoos, serums and treatments with active ingredients such as ketoconazole, saw palmetto or caffeine are offered as solutions to combat hair loss.
- Hair growth supplements: Over-the-counter supplements containing vitamins, minerals and herbs such as biotin, vitamin D or omega-3 fatty acids can support hair health.
- Hair care practices: Gentle care, avoiding heat treatments and a balanced diet help to keep hair healthy.
- Camouflage techniques: Styling techniques, hair fibers and special products create visually thicker hair.
- Lifestyle changes: Stress reduction, better nutrition and exercise have a positive effect on hair health.
The effectiveness of these methods varies from person to person. A consultation with our medical staff can help you find the right method.