Anabolics, testosterone and hair loss: is there a correlation?
Anabolics, testosterone and hair loss: is there a correlation?
Many people who take anabolic steroids or testosterone supplements sooner or later ask themselves whether these substances can trigger hair loss. Especially when suddenly more hair appears in the sink or on the pillow.
This concern is justified, because certain hormonal changes act directly on the hair follicles. In this article, we explain clearly and understandably the roles that testosterone, DHT and genetic factors play, why some people are more affected than others, and how you can strengthen your hair despite hormonal changes.
What are androgens and what do they do in the body?
Androgens are male sex hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). They regulate many physiological processes in the body, including:
- Muscle growth and fat distribution
- Libido and reproduction
- Hair growth and sebum production
Important to know:
A portion of testosterone is converted into DHT by the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. This conversion is physiologically meaningful because DHT fulfils certain tasks more strongly than testosterone.
However, how DHT acts in the body depends not only on the amount produced but especially on the genetic properties of the androgen receptors.
What function does DHT have in the body?
DHT regulates many physiological processes:
- Prostate development and function
- Activity of the sebaceous glands
- Development of male characteristics during puberty
- Body hair growth
- Muscle and bone stability
What happens when testosterone and DHT levels rise too much?
Everyone needs testosterone and DHT in a certain balance for the body to function normally. When taking anabolic steroids or testosterone supplements, testosterone levels rise sharply. Part of this excess is converted into DHT by the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, causing DHT concentrations to rise far above normal physiological levels.
Mechanism in people with genetically sensitive androgen receptors:
- Hair follicles react more strongly / more sensitively to DHT.
- With elevated DHT levels, too much DHT binds to these receptors.
- The follicles become overstimulated.
- The biological signals within the follicle change.
- The growth phase (anagen phase) shortens.
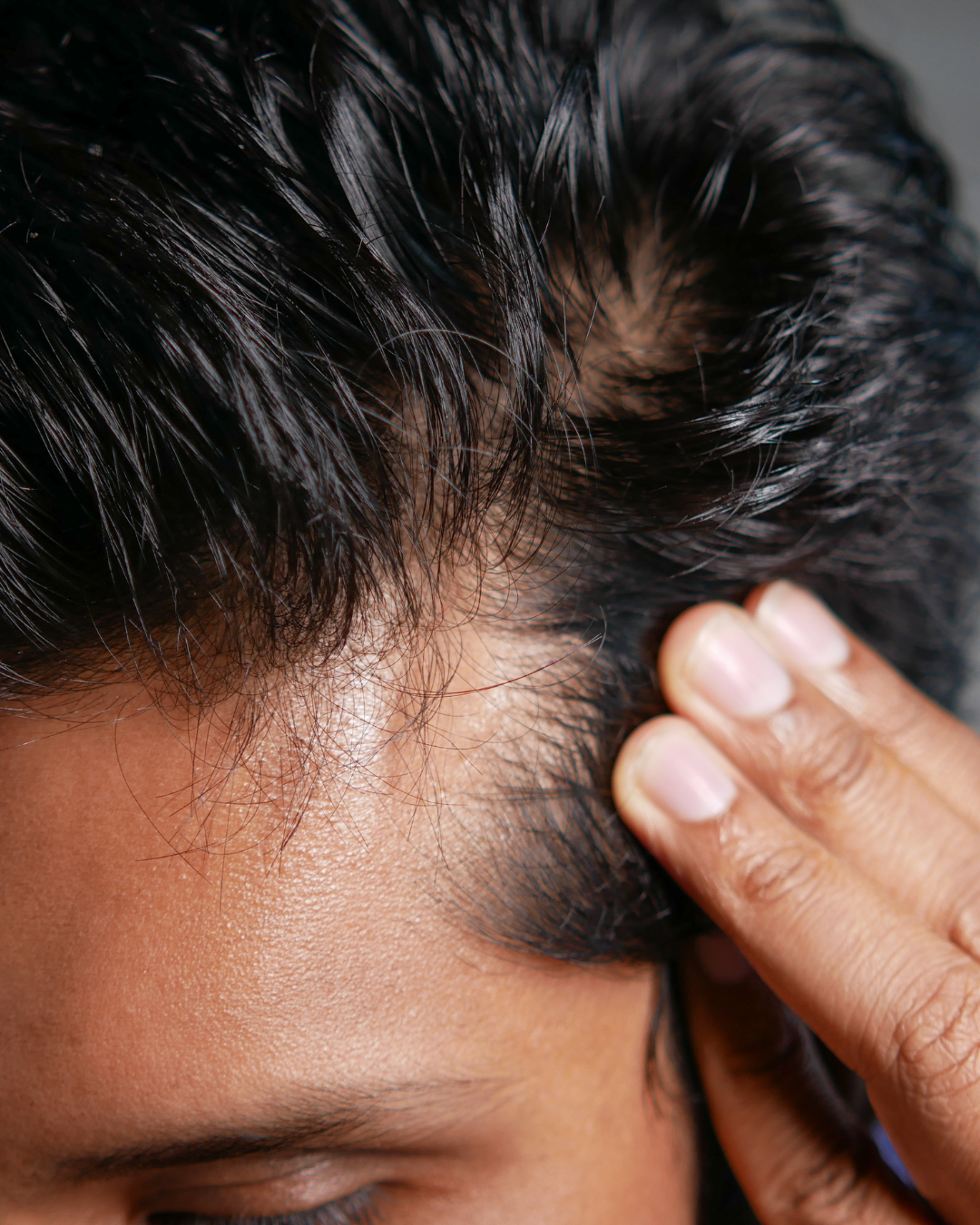
- The follicles miniaturize.
- Hair becomes thinner and falls out earlier.
Result: Hair follicles that are sensitive to DHT show increased miniaturization, thinning hair and ultimately hair loss. This effect can also occur in people without a genetic predisposition to hereditary hair loss.
Dr. Balci says:
“Testosterone is essential for life. An excessively high level, caused by anabolic steroids, increases DHT concentration and activates a biological mechanism through overstimulation that causes the hair follicles to shrink. While androgen receptors are generally more strongly stimulated, genetically sensitive androgen receptors trigger an exaggerated reaction that initiates a cascade of additional mechanisms. These ultimately lead to miniaturization of the hair follicles and shortening of the hair-growth phases, which in the long term results in typical hair thinning and hair loss. Miniaturization often begins at the temples and crown because these areas are particularly sensitive, but it essentially affects the entire top of the head.”
How to support the hair follicles
Even with elevated DHT levels, the hair follicles can be supported:
- PRP treatments: supply the hair roots with nutrients, promote healing and growth
- Gentle hair care: no aggressive chemicals, gentle brushing and combing
- Healthy, balanced diet: ensure adequate intake of protein, zinc, selenium, iron and vitamin D
- Stress reduction: chronic stress can accelerate hair loss
How to stabilize hormone balance
If hormone levels are out of balance, there are various ways to counteract hormone-induced hair loss and protect the hair follicles:
- Reduction or discontinuation of anabolic steroids (under medical supervision)
- Supporting regeneration: sleep, rest periods, sufficient calories and nutrients
- PRP to strengthen the hair follicles that are sensitive to DHT
- Regular blood tests to monitor testosterone and DHT levels
Most important of all is a professional assessment to determine whether the hair loss is truly hormone-induced or whether other causes are present.
Key takeaways
Androgens such as testosterone and DHT are natural and important hormones. Only when they are massively increased through the use of synthetic substances like anabolic steroids can an imbalance occur that stresses genetically sensitive hair follicles. An excessive DHT stimulus causes the follicles to overreact, shorten their growth phases and miniaturize. This can also affect people without a family history of hair loss.
A medical assessment, hormonal stabilization and supportive treatments such as PRP help slow down or stabilize the process.
If you are taking anabolic steroids and are unsure whether your hair loss is related, you can contact us at any time. We will provide competent, individual and discreet advice.